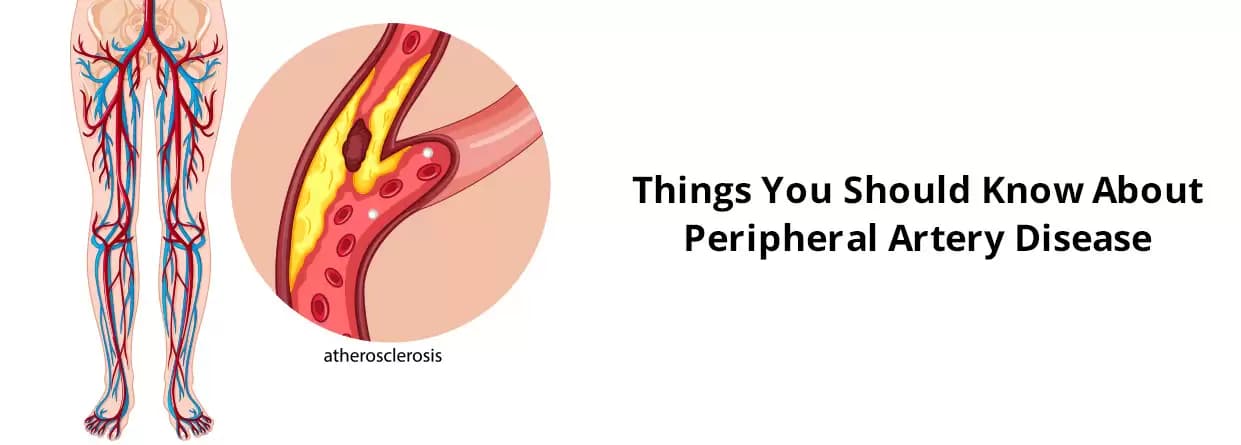
Peripheral artery disease or commonly referred to as peripheral vascular disease is the accumulation of fat and cholesterol (plaque) in the arteries in your legs or arms. The condition makes it harder for the blood to carry oxygen and nutrients to the tissues and organs surrounding the legs and arms. Peripheral artery disease (PAD) develops gradually, and slowly, narrowing your arteries.
Cardiac issues are one of the most common medical conditions that affect a majority of the population in India and across the world. One of the most prominent is peripheral artery disease which constitutes about 40 to 50 million cases in India. Peripheral artery disease is a medical condition which leads to the build-up of plaque in the arteries around the legs and arms.
The condition occurs when the arms and legs do not receive enough blood to function properly.As per one study, it is identified that more than 200 million people are affected by this condition across the world. So, if you suspect that you might have PAD, then make sure to book your appointment with the best cardiologists in Kolkata, BM Birla Heart Research Center. You will find the most experienced and expert professionals who will ensure the best diagnosis and proper treatment solution that’s right for you.
This blog contains information on peripheral artery diseases and how you can manage symptoms relate to the condition. Please note that this blog is for informational purposes only and does not replace the importance of a cardiology doctor’s consultation.
Peripheral artery disease commonly referred to as peripheral vascular disease is the accumulation of fat and cholesterol (plaque) in the arteries in your legs or arms. The condition makes it harder for the blood to carry oxygen and nutrients to the tissues and organs surrounding the legs and arms. Peripheral artery disease (PAD) develops gradually, and slowly, narrowing your arteries.
PAD is a medical condition that causes pain in the legs as you begin walking or exercising. The pain occurs due to insufficient oxygen and blood in the leg muscles. Patients with PAD usually complain of sore feet or legs. In the case of severe PAD, these sores can also turn into dead tissues (gangrene) which may require amputation.
The plaque or blood clots block or narrow the peripheral arteries which do not allow the oxygenated blood to nourish organs and tissues in the legs and arms. Depending on the severity of the condition, doctors classify PAD types based on the stages. Stage I PAD is asymptomatic which means the patients may not experience any symptoms. Stage II PAD usually includes mild to severe claudication which is basically leg pain during exercise. Stage III refers to the pain in your legs even while you’re at rest. Finally, stage IV is the ulcers or gangrene which generally requires amputation.
Furthermore, certain medical conditions like atherosclerosis also affect peripheral arterial disease. Doctors also associate certain risk factors like consuming tobacco products, having diabetes, being 50 years and above, having a family history of heart diseases, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, abdominal obesity, blood clots, kidney disease, etc. which can increase the risk of peripheral artery disease.
Peripheral Artery Disease symptoms usually vary from one patient to another. Most people may not experience any signs until later in life. For most people, symptoms may not become apparent until the artery gets narrowed by 60% or more. Patients with PAD initially complain of pain, cramping, or discomfort in the legs or around the buttocks. The pain and discomfort usually go away while you’re resting. Additionally, common peripheral artery disease symptoms include -
Early detection of peripheral artery disease (PAD) is important so that the doctor can begin the treatment as soon as possible.
Peripheral artery disease usually occurs gradually and is often hard to distinguish. The doctor may examine your symptoms and assess your medical history report. Any blockage in the blood vessels can be determined by diagnostic tests. Peripheral artery disease tests involve the following -
While some symptoms of PAD are mild to moderate, the treatment focuses on preventing the condition from progressing further. For severe symptoms, the doctor suggests surgical procedures that can provide long-term health benefits and reduce the chances of recurrence.
Medications can help improve peripheral artery disease symptoms. The doctor usually prescribes cholesterol drugs, blood pressure medicines, and medicines to control blood sugar and clots to improve blood flow and manage pain. If all these medicines and lifestyle changes are not effective in treating the condition, the doctor may recommend surgery. In some cases, angioplasty or surgery may be necessary for treating peripheral artery diseases. Here are some common surgical procedures to treat clogged arteries -
While surgical procedures offer long-term health benefits and reduce the chances of recurrence, certain lifestyle changes also contribute to preventing the condition from getting worse. Exercising daily, taking good care of the foot, maintaining a healthy diet and weight, etc. can reduce the risk of complications.
Peripheral artery disease is a condition that can trouble you for the rest of your life. Although there’s no permanent cure for PAD if the condition becomes severe, there are still ways you can manage it and prevent it from getting worse. Here is how you can prevent peripheral artery disease
Peripheral artery disease is not untreatable and can be managed with certain options. Discuss your symptoms with the cardiology doctor for an early diagnosis and effective treatment.
Depending on the type of treatment and the severity of the condition, you may require a few days to recover from the surgical procedures. It usually takes six to eight weeks to recover completely from peripheral artery surgery. Consult your doctor if you are experiencing any issues after your procedure to reduce the chances of complications.
Possible complications of untreated PAD include -
Minimally invasive procedures for peripheral artery disease treatment include -
Yes, some researchers believe that peripheral artery disease symptoms can be reversed with lifestyle changes and dietary restrictions. However, it depends on the medical condition of the patient and how strictly they follow preventive measures.
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) can be treated with several minimally invasive methods like angioplasty, exercise therapy, medication to control risk factors, and in severe cases, surgical bypass or amputation.
Yes, as peripheral artery disease (PAD) can cause a reduction in blood flow to the limbs, ulcers, tissue damage, and, in severe cases, loss of limb.
There is no known cure for peripheral artery disease (PAD) but can be efficiently managed with medication, lifestyle changes, and clinical interventions to improve symptoms, slow the disease's growth, and reduce complications.
Involving a healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise, eating a balanced diet, quitting smoking, controlling blood pressure and cholesterol, and managing diabetes helps to prevent peripheral artery disease.
Asymptomatic peripheral artery disease (PAD), claudication (pain during exercise), rest pain, and critical limb ischemia (severe pain at rest with risk of tissue damage) are the four stages of PAD.
Written and Verified by:

Dr. Ashok B. Malpani is a Senior Consultant in Cardiology Dept. at BM Birla Heart Hospital, Kolkata, with over 34 years of experience. He specializes in complex angioplasty, primary angioplasty, and pacemaker implantation.
Similar Cardiology Blogs
Book Your Appointment TODAY
© 2024 BMB Kolkata. All Rights Reserved.