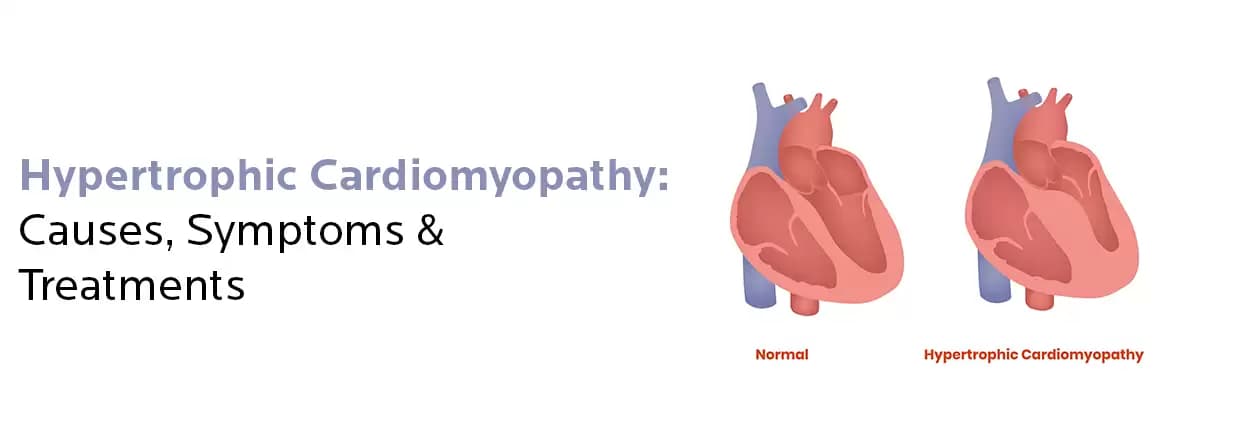
A genetic heart condition called hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is determined by unusual thickening of the heart muscle, specifically the left ventricle.
Do you feel chest pain, shortness of breath, or irregular heart rhythms? Well, these symptoms should not be overlooked in any way as they might indicate hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. In this condition, the heart muscle in the left ventricle thickens unusually. This condition can be caused by different factors like age, genetic mutations, high blood pressure, hormonal influence, etc. It is among the rare conditions, but once is diagnosed, it must not be left untreated as it can pose serious complications.
If you suspect that you might have this condition, book your appointment with highly professional cardiology experts in Kolkata at the BM Birla Heart Research Center. You will discover the right diagnosis and treatment options.
In this blog, for your enhanced comprehension, we will involve a discussion on hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, its causes, symptoms, and treatment options. Please be aware, though, that this article is meant only for informative purposes, and we do not advocate skipping the cardiology doctor's consultation in any way.
A genetic heart condition called hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is determined by unusual thickening of the heart muscle, specifically the left ventricle. This thickening leads to stiffness affecting how well the heart pumps blood. Particularly in young athletes, HCM raises the risk of arrhythmias and abrupt cardiac arrest. However, they can vary, some symptoms are fainting, shortness of breath, and chest pain.
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is not a very common condition and affects 1 in 500 persons globally. Nonetheless, it is the most prevalent hereditary cardiac disorder, and several groups may have varied prevalence rates. Since HCM is usually inherited, initial diagnosis and genetic screening are vital.
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy symptoms might vary depending on person to person. Here are some of the common symptoms of this condition:
Several probable causes are there for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Here are some of them:
To diagnose hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, the healthcare professional first begins with evaluating the patient’s overall health, learning about the symptoms, and medical history of the patient. Depending on the assessment, here are the following tests that are ordered to confirm the diagnosis:
Depending on the symptoms of the patient and medical history, here are some of the options that are taken into account for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy treatment:
In conclusion, the management of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy requires a personalized strategy that involves medication, surgical procedures, and lifestyle modifications. A comprehensive medical assessment, including genetic testing, is vital for immediate diagnosis. Regular monitoring and follow-up are important, irrespective of the treatment plan chosen like medication, alcohol septal ablation, septal myectomy, or, in the worst situations, a heart transplant. To manage life with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and ensure the best results, it is recommended to get in touch with people knowing lifestyle changes and available treatments.
The majority of patients with HCM have normal life expectancy and they do not experience any serious complications.
Yes, HCM can be cured by managing the symptoms through medications, lifestyle changes, septal myectomy, alcohol septal ablation, etc. However, in a rare or severe case, there might be a need for heart transplantation.
Written and Verified by:

Dr. Shuvo Dutta is a Senior Consultant in Cardiology Dep. at BM Birla Heart Hospital, Kolkata, with over 34 years of experience. He specializes in radial and femoral angioplasty, complex cardiac interventions, and was the first in India to perform carotid artery stenting to prevent brain stroke.
Similar Cardiology Blogs
Book Your Appointment TODAY
© 2024 BMB Kolkata. All Rights Reserved.