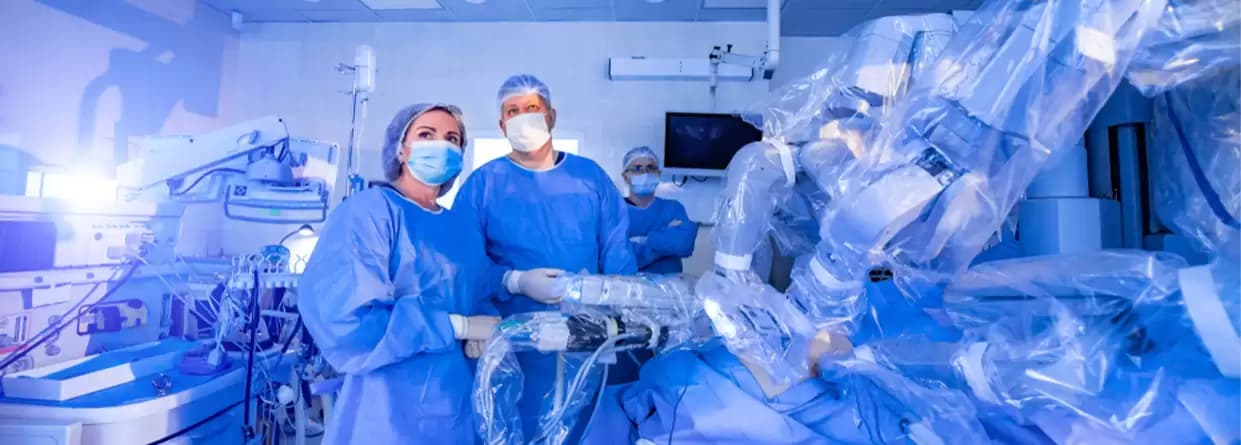
Robotic surgery or robot-assisted surgery is an innovative method, associated with non-invasive or minimally invasive surgeries such as laparoscopy.
Robotic surgery or robot-assisted surgery is an innovative method, associated with non-invasive or minimally invasive surgeries such as laparoscopy. A surgical robot is a device controlled by a computer which has been programmed to help the placement and usage of surgical instruments. The most widely used robotic surgical procedure involves mechanical and camera arms, containing surgical instruments controlled by the surgeon from a computer. The surgery is being increasingly accepted since it allows better clarity, and high-definition vision of the surgical site and also allows conducting complex procedures with enhanced precision, flexibility, and control.
Robotic laparoscopic surgery has been conducted since the 1980s to overcome the limitations of a general laparoscopy such as a two-dimensional view, partial articulation of surgical instruments, and lack of efficiency. Robotic laparoscopic surgery helps to overcome these limitations and convert invasive surgeries such as laparotomy into minimally-invasive methods.
Several advantages of robotic laparoscopic surgery include:
Some laparoscopic surgeries that have been successfully done through the robotic technique are:
Complications
Robotic laparoscopic surgery has rare complications, though some general problems that may arise during or post the surgery include:
A few factors increase the likelihood of complications in Robotic Laparoscopic Surgery. These factors include:
All factors must be discussed with the doctor before the surgery to avoid serious problems.
Similarly, like normal laparoscopic surgery, even in Robotic Laparoscopic Surgery, the doctor will conduct physical exams and several other tests such as blood tests, urine tests, ECG, X-ray, ultrasound, or a CT scan to assess the condition of the organ.
All current medications, health problems, and allergies must be discussed with the doctor beforehand and medications, diet, etc. as suggested by the doctor must be taken as advised. Moreover, family or friend assistance must be called for.
Before beginning the procedure, the doctor will place the patient under anesthesia – general or local – depending on the intensity of the procedure. Post this, the doctor makes small incisions, also called keyhole incisions to allow carbon dioxide to enter the abdomen for it to expand, making it easier to visualize the area.
Post this, an endoscope is inserted into the area through one of the incisions, which provides clear, magnifying images of the organ on a monitor. This endoscope is attached to a robotic arm, while the other robotic arm holds forceps, scissors, dissectors, and scalpels – needed to hold, cut, dissect, and close the surgery. All this while, the doctor monitors the screen images and then guides the robotic arms to perform the surgery. The surgery is about 1-2 hours long and does not cause pain because of the influence of anesthesia. However, even post-operative pain is very less and can easily be managed with some medications. That said, gas problems might occur for a few days post-surgery but will eventually smoothen. A person recovers easily within 3-5 days and can resume normal, routine activities post-complete recovery unless there are any complications.
Post the procedure, the doctor will also advise on the steps to be followed to enhance recovery and ensure no complications. You may be advised to:
Also, it is also important to understand the alarming symptoms that must be noted, if they appear to post a robotic laparoscopic surgery. Some of the symptoms that would need you to call the doctor are:
Overall, the benefits of a robotic laparoscopic surgery outweigh the few, rare complications and risks. However, each case needs to be evaluated individually; hence, advice from a doctor should be taken before deciding on the procedure.
Written and Verified by:

Director Exp: 25 Yr
General Surgery, Minimal Access & Bariatric Surgery
Dr. Rajesh Sharma is a highly acclaimed robotic and minimally invasive surgeon in Jaipur with over 20 years of experience and 15,000+ advanced surgical procedures to his credit. A pioneer in Rajasthan, he was the first surgeon in the state to be appointed as a Robotic Surgery Proctor for the da Vinci Surgical System and has performed the highest number of robotic general surgeries in Rajasthan.
Similar General Surgery Blogs
Book Your Appointment TODAY
© 2024 RBH Jaipur. All Rights Reserved.