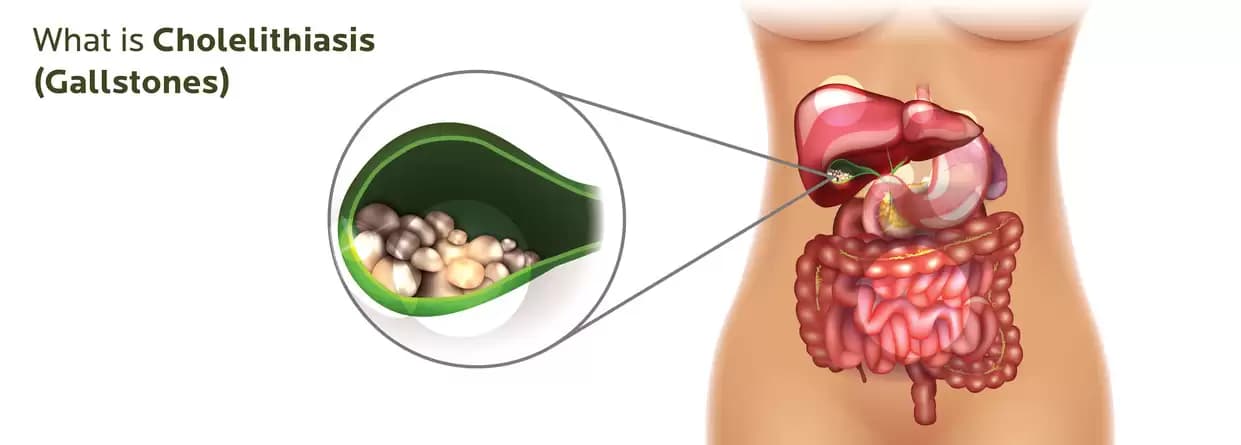
Gallbladder stones or Choleliathiasis are stone-like objects that form in the gallbladder as bile ducts. Bile is a fluid that is produced by the liver and is made up of several substances. These substances are bilirubin and cholesterol which are stored or released by the gallbladder and help in digesting fats.
Do you feel intermittent pain in the upper right part of your abdomen?? Does it last for more than one to five hours? Can you feel the pain in your back and shoulder? If yes, then it could indicate gallstones (Cholelithiasis) in your gallbladder. Well, one of the most common digestive problems around the world is gallbladder stones. As per one study, it is found that in most developed countries, an estimated 10%-15% of people have gallbladder stones. The gallbladder is located under the liver on the right side of the abdomen and resembles the shape of a small pear.
Gallbladder stones or Choleliathiasis are stone-like objects that form in the gallbladder as bile ducts. Bile is a fluid that is produced by the liver and is made up of several substances. These substances are bilirubin and cholesterol which are stored or released by the gallbladder and help in digesting fats.
Gallstones can cause pain depending on the number and size. It may vary from the size of a tiny grain of sand or maybe as large as a golf ball. However, no combination of number and size can predict whether symptoms will occur or not and the severity of the symptoms. Usually, the treatment option for gallbladder stones is surgery, but it is recommended depending on the severity of the symptoms the patient is experiencing.
In this blog, we are going to discuss everything related to Cholelithiasis.
Gallstones also known as Cholelithiasis are hard deposits of cholesterol and other substances that look like pebbles. These occur in various sizes. The size varies as small as a tiny grain of sand and is not so harmful if in the initial stages. Sometimes, it can occur in large sizes like golf balls.
These stones can be composed of one or a mixture of substances. The normal pieces are a mix of calcium bilirubin, cholesterol, and calcium carbonate. They regularly fall under one of three characterizations. Blended stones are composed of a cholesterol substance of 20-80% of the mass of the stone.
Pigment stones are under 20% cholesterol. They are composed of calcium salts and bilirubin. They have dark shade and are normally small. Cholesterol stones have a body weight of at least 80% cholesterol. They commonly have a dark focal spot and are brownish, dull green, or yellow.
There are two types of gallstones (Cholelithiasis) which include:
Some of the Choleliathiasis causes are listed below:
If you have any of the following symptoms, you must consult a medical professional immediately.
The risk factors for gallstones are:
Your doctor will order the following tests for gallstones diagnosis:
This device uses a special scope with an ultrasound probe on the end. The scope is passed down into the small intestines where internal bile ducts, gallbladder, and pancreas ultrasound images can be taken. It helps locate bile duct stones that may be missed by ordinary ultrasound. The test also assists in diagnosing cancers within the pancreas and bile ducts.
A simple test named "Ultrasound abdomen" performed by the radiologist on an OPD
basis quickly detects gallbladder stones' number and size, location, and associated complications. It is quite safe, noninvasive low cost, and safe even in pregnancy.
Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is a special type of endoscope, which allows access to the bile ducts and pancreas. It is performed by removing stones from the bile ducts or pancreas.
Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) is a test that involves using a machine called MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging). A non-invasive test, it employs special computer software for producing images of the bile and pancreatic ducts similar to the images gathered by ERCP and doesn’t need an endoscopy. Anomalies found on MRCP can be further evaluated or treated by ERCP or surgery.
All patients with the above-mentioned symptoms are treated surgically if they are young and medically fit.
In the present era, where various surgical modalities are quite safe and with improved outcomes due to minimally invasive procedures, even people are getting treated for asymptomatic gallstones surgically depending on the age of the patient, medical fitness, occupational profile and size of the stone with associated lesion and family history of Gastrointestinal or Gall bladder malignancy. If a doctor suspects that you are at higher risk for surgical complications, then
there are various surgical and non-surgical methods for gallstone treatment.
Here are surgical options that might be considered:
Non-surgical treatment
If surgery cannot be considered due to any specific reason, then here are other non-surgical treatment options the doctor will consider:
Gallstones or Cholelithiasis are common these days and usually, they are never a cause of concern. You will probably never know that the stones are there if they stay put in the gallbladder. They become dangerous, once they start to move. It is important to know that these tiny, pebble-like pieces can harm and can enter into the tight spaces of the delicate biliary system.
A gallbladder attack can be severe and dangerous at the same time, primarily if you don’t know that you have gallstones. In such cases, the recommended treatment option is surgery. It is crucial to understand the symptoms of gallstones and obtain information. Speak to the best gastroenterologist in Jaipur to learn more about the options and what’s suitable for you.
Usually, gallstones or Cholelithiasis is not dangerous, but if they enter the bile duct and the treatment is ignored, then it can cause blockage in the pancreatic duct leading to pancreatitis. It can cause severe, continuous abdominal pain, and needs hospitalization. People having a history of gallstones are at higher risk of gallbladder cancer.
A few varieties of gallstones like pure cholesterol stones can be dissolved by medication but they should be small because it takes a long time for medical therapy to dissolve the gallstones and at the same time medical therapy is only indicated where surgery is not an option. However, the majority of patients have mixed stones in their gall bladder which cannot be dissolved by medication.
It is very simple to reduce the risk of developing gallstones. All you need to do is make some changes in your life such as:
Written and Verified by:

Dr. B D Soni is a Consultant in Gastrointestinal Surgery at CK Birla Hospital, Jaipur, with over 7 years of experience. He specializes in GI oncology, laparoscopic ventral hernia surgery, thoracoscopic esophageal surgery, and pancreaticobiliary procedures.
Similar Gastro Science Blogs
Book Your Appointment TODAY
© 2024 RBH Jaipur. All Rights Reserved.