Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH), also as referred to as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is among the most common conditions that affects around 50% of men who are above 50 and up to 90% of men over 80. It is normal for the prostate to become enlarged as men age. This enlargement can cause several urinary symptoms like painful urination, difficulty urinating etc., affecting the quality of life of an individual. If you are experiencing such symptoms, book your appointment with one of the best urologists in Kolkata at The CMRI.
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH), also as referred to as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is among the most common conditions that affects around 50% of men who are above 50 and up to 90% of men over 80. It is normal for the prostate to become enlarged as men age. This enlargement can cause several urinary symptoms like painful urination, difficulty urinating etc., affecting the quality of life of an individual. If you are experiencing such symptoms, book your appointment with one of the best urologists in Kolkata at The CMRI.
This blog will explore the nature of BPH, its types, symptoms, causes, risk factors, diagnosis, and treatment options. Understanding these aspects of BPH helps in the early detection, efficient management, and enhancement of the quality of life for men affected by this condition. However, kindly note that this blog is for informational purposes and does not replace the significance of a urology doctor consultation.
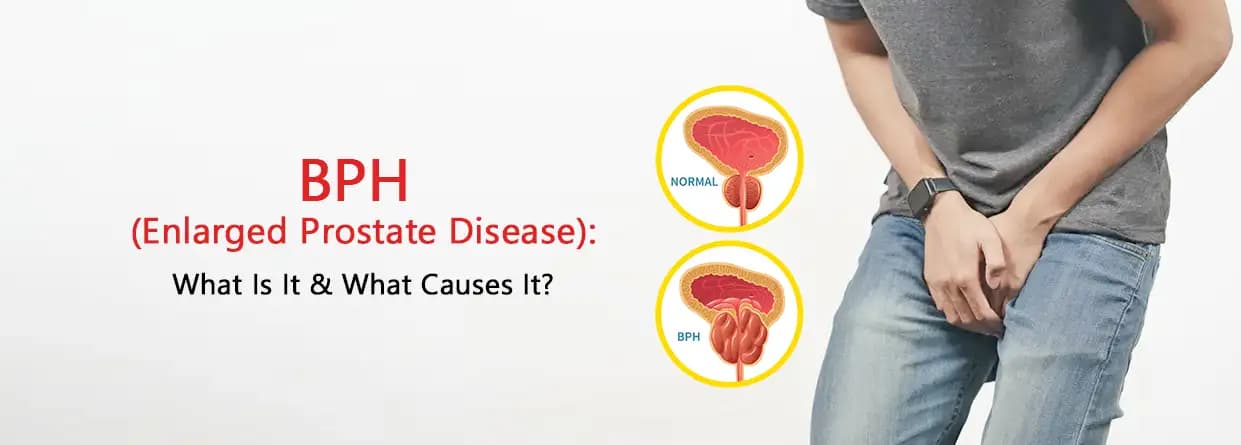
Enlarged Prostate Disease or Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) is a benign condition causing an increase in the prostate gland size. The prostate is a gland that appears as a small, walnut-sized in the male reproductive system, positioned near the bladder and the rectum front. It encircles the urethra, a tube through which urine flows out of the bladder. The exact cause of enlarged prostate disease is not known, but it is identified that growing age and hormonal changes are the main contributors. As the prostate enlarges, it can put pressure against the urethra and bladder base causing urinary problems.
Prostate enlargement disease is categorised into two main types that are:
When enlarged prostate disease causes the prostate to grow, then it causes obstructions in the urethra. The symptoms occur because the enlarged prostate gland presses against the urethra, narrowing it and making it harder for urine to pass through. As a result, the symptoms of enlarged prostate disease include:
The precise cause of enlarged prostate disease is unknown, but several factors are determined to contribute to developing the enlarged prostate disease:
Certain factors increase the risk of developing BPH:
Here is what healthcare professionals do to diagnose enlarged prostate disease to rule out other conditions and ensure the presence of an enlarged prostate:
The treatment for enlarged prostate disease depends on the extent of symptoms and the impact on quality of life. Some of the effective treatment options recommended are:
Enlarged Prostate Disease, or Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH), is among the most common conditions that affect ageing males. Even though the exact cause is not completely understood yet, various factors including ageing, hormonal variations, genetics, and lifestyle, contribute to its growth. Symptoms of this condition range from mild to severe, affecting the quality of life of an individual and causing complications if left untreated. With proper diagnosis and effective treatment, most males can find relief from symptoms and maintain a good quality of life.
There is no cure available for prostate enlargement disease, or BPH, but is manageable with medications, minimally invasive procedures, or surgery. Treatment helps relieve symptoms and improve quality of life rather than removing the condition.
Prostate enlargement disease is not a dangerous condition but can cause serious complications such as urinary retention, bladder infections, and kidney damage if not treated on time. Immediate management is essential to avert these problems.
Prostate enlargement does not lead to erectile dysfunction, but the linked symptoms and treatments, specifically certain medications and surgeries, can impact sexual function in some males.
Prostate enlargement cannot be reversed, but its symptoms can be efficiently managed and mitigated with proper treatment, including lifestyle changes, medications, and medical procedures.
The prostate enlargement often does not cause pain. However, complications like urinary tract infections or bladder stones that result from BPH can cause discomfort or pain.
Written and Verified by:

Dr. Pankaj Kumar Gupta is a Consultant in Urology Dept. at CMRI, Kolkata with over 10 years of experience. He specializes in renal stone management, prostate & uro-oncology surgery, reconstructive urology including urethroplasty.
Similar Renal Sciences Blogs
Book Your Appointment TODAY
© 2024 CMRI Kolkata. All Rights Reserved.