Dengue hemorrhagic fever is linked to the secondary dengue infection, which implies that the person is infected with another serotype of dengue virus than before resulting in a more severe form of dengue virus.
If you experience a sudden high fever or chills, book your appointment with one of the best doctors in Jaipur at CK Birla Hospitals. You will find the proper diagnosis with the right solutions here.
Dengue hemorrhagic fever is linked to secondary dengue infection, which implies that the person is infected with another serotype of dengue virus than before resulting in a more severe form of dengue virus. As per WHO’s study, an estimated 300 million infections are asymptomatic for every 100 million symptomatic dengue cases occurring every year. Essentially, dengue is an arthropod-borne disease that is caused when one of the four serotypes of dengue virus infects the person; infection by one of the dengue viruses immunes a person from the serotype for the whole life and this infection is known as primary infection which is not very severe and easily manageable with directed cure.
However, if a person, who has had a primary infection before, is later infected by any of the other three serotypes of the dengue virus, a severe complicated version of dengue emerges that is known as dengue hemorrhagic fever. Repeated exposure to the dengue virus makes one more prone to developing dengue hemorrhagic fever. We will offer you comprehensive information on dengue hemorrhagic fever in this blog so stay tuned. However, kindly note that this blog is for informative purposes only and we do not construe the healthcare professionals' consultation in any way.
Dengue fever is a mosquito-borne viral disease caused by four closely related viruses, which spread through the Aedes mosquitoes. The fever is spread through the bite of an Aedes mosquito that is carrying the dengue virus. This species of mosquito can breed inside or outside the house in containers holding water and cannot fly more than 200 meters away from its place of birth. The Aedes Mosquito is most active during the early hours of the morning and before sunset. Dengue fever is extremely painful, and debilitating and often causes high fever, along with headache and extreme muscle or joint pain. The fever rarely causes death; however, it can progress into a serious form known as Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever.
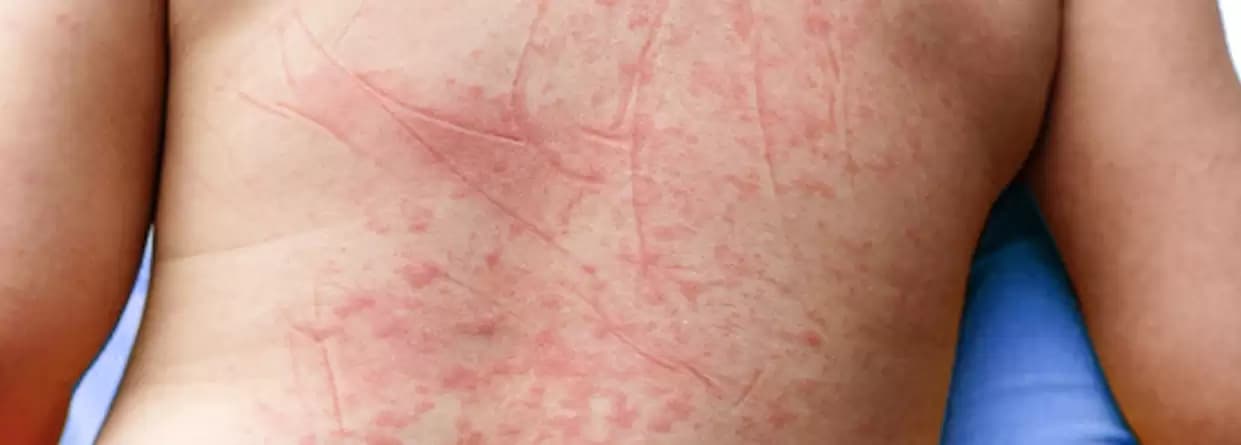
A person infected with the dengue virus can experience symptoms such as:
A person may be recovering from these dengue symptoms and might develop severe new symptoms, which could indicate dengue hemorrhagic fever. These symptoms include:
People at high risk of developing dengue hemorrhagic fever
The doctor will check for symptoms and analyze the type of virus that has infected. The first primary infection will be diagnosed and then studied further to detect dengue hemorrhagic fever. The doctor might also conduct a few tests to diagnose the infection, these tests or checks include:
Moreover, you would need to specify your medical history, family history, lifestyle, recent travels, etc.
There is no specified treatment or vaccination for dengue or dengue hemorrhagic fever. However, the treatment objective is to manage symptoms and prevent the infection from worsening further. These treatments include:
Moreover, the doctor will suggest rest and frequent hydration to keep the symptoms from getting worse. Symptoms of dengue hemorrhagic fever are the most difficult to manage since they are more intense and appear at a faster rate.
What are the prevention tips for Dengue hemorrhagic fever?
The best way to prevent dengue hemorrhagic fever is to stay away from mosquito bites and stop the birth and breeding of Aedes mosquitoes. The following preventive methods can help stop the breeding of dengue carriers:
Further, protect the patient (from any further mosquito bite) that has been infected by the virus, since that could cause the spreading of the virus if the infected mosquito, in turn, bit another person.
Dengue hemorrhagic fever can cause:
In summary, dengue hemorrhagic fever remains a serious global health risk, mainly in areas where the Aedes mosquito is common. To minimize its impact requires early detection, prompt medical intervention, and watchful mosquito control. Campaigns to raise public awareness assist in preventing this disease. In addition, it is vital to continue researching vaccines and efficient therapies. Governments, healthcare providers, and communities need to work together to fight this probable dangerous disease and protect public health across the globe. If you are diagnosed with dengue hemorrhagic fever, ensure working with your doctor for fast relief.
No cure is available for dengue hemorrhagic fever, however, with early clinical intervention symptoms and complications can be mitigated.
Dengue fever general affects bone marrow declining its efficiency to form red blood cells causing reduction in hemoglobin levels, eventually results in anemia.
Yes, humans can contract dengue fever from one another through the bite of an infected Aedes mosquito, mainly Aedes aegypti.
Written and Verified by:

Dr. Sushil Kalra is the Director of Internal Medicine Dept. at CK Birla Hospital, Jaipur, with over 34 years of medical experience. He specializes in critical care, managing ICU and CCU patients, and acute medical conditions.
Similar Internal Medicine Blogs
Book Your Appointment TODAY
© 2024 RBH Jaipur. All Rights Reserved.