
 Ambulance Services: 07340054470
Ambulance Services: 07340054470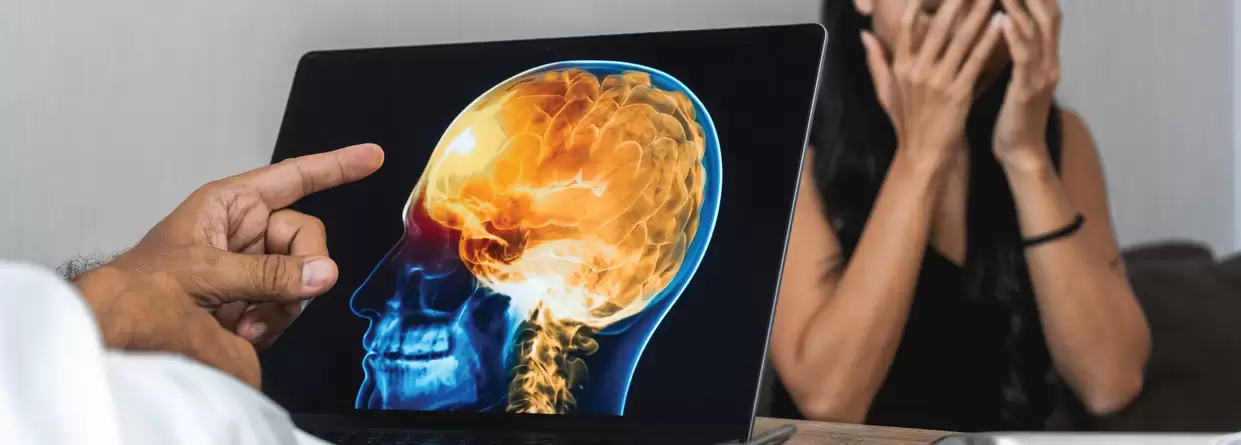
Neurosciences | Posted on 03/23/2020 by RBH
Head injuries are one of the most common causes of injuries and deaths in adults. People end up in accidents and violent situations. Sometimes, an unfortunate tackle on the field results in a brain injury which might end up changing one’s life course. Here are a few things you ought to know about our brain and things which may harm it.
A traumatic brain injury occurs when a sudden trauma, often a blow to the head or a penetrating head injury, damages tissue and disrupts the normal function of our brain. Its symptoms can be categorized from mild to severe. A mild traumatic brain injury can be a minor concussion and a severe traumatic brain injury can cause a coma and sometimes death.
A concussion can cause momentary loss of consciousness, dizziness, confusion, loss of one’s equilibrium, headache, and vision problems. A moderate traumatic brain injury leaves a person lethargic and unconscious. They only respond to stimuli. A severe traumatic injury can cause both short-term and long-term effects which can impair cognitive and motor function, sensation, and behavior. It has major impacts on one’s family and societal relationships.
Brain tumors, infections, or a stroke do not come under the category of traumatic brain injuries.
Closed Brain Injury: This occurs when the brain experiences a non-penetrating injury without a break in the skull. This is often caused by a rapid backward and forward movement of the brain inside the skull, which results in bruising, and tissue damage and disrupts normal brain function.
Penetrating brain injury: Open head injuries occur when there is physical trauma, which penetrates the skull. For example, when a bullet pierces the brain, or a sharp object penetrates the skull during an accident.
The symptoms of Traumatic Brain Injuries fall under four major categories,
Some of the leading causes of Traumatic Brain Injury include:
In the military, the leading causes of Traumatic Brain Injury are bullets, fragments, blasts, falls, motor vehicle crashes, and assaults.
Do people make full recovery after a Traumatic Brain Injury?
According to several studies conducted in this area, once the brain cells are damaged or degenerated because of an injury, they do not regenerate. Despite this, younger people have shown a better recovery rate than other age groups. Studies have also noted that other parts of the brain compensate for the damaged tissue or the synapses find alternative pathways to deliver the messages. As each brain injury is unique, the recovery time for each is different and can often take years or may sometimes require a lifelong rehabilitation process.
Results of a Traumatic Brain Injury
Severe injuries may leave a person with lifelong deficits, which can be classified into cognitive, motor, sensory, communication, functional, social difficulties, regulatory disturbances, personality changes, and epilepsy.
Cognitive deficits include amnesia, decreased attention span, coma, and difficulty in following two or more steps commands. Paralysis, Poor balance, decreased endurance, inability to plan motor movements, delays in initiation, tremors come under motor deficits.
People who have experienced head injuries often complain of regular migraines, fatigue, and changes in sleeping and eating habits.
Epilepsy too is a major after effect of head injuries. Though in most cases, seizures occur immediately after the injury or within the first year. Though it is possible for it to resurface years later.
Brain injuries do not necessarily result in long-term defects. Though correct diagnosis and treatment on time play a major role in a person’s recovery. Successful rehabilitation depends on the following variables: –
The overall health of the patient needs close monitoring with the help of doctors and family members. The patient needs all-around care and medical observation by a specialist team of doctors.
It is of utmost importance that friends and family support the patient affected by the injury. They can do this by spreading positive reinforcements to help the patient slowly get back to a daily routine before the injury or in some cases help them settle into a new one.
Brain injuries often damage the nerves responsible for coherent speech in a person. A speech therapist helps the patient slowly regain their speech patterns and improve pronunciation.
It is a vital part of recovery that helps improve flexibility and range of motion after the injury. It minimizes scar tissue in case of surgeries and helps with the pain without prescription drugs.
Occupational therapy helps the patient adapt to their new lifestyle through various means and equipment. It plays a major role in getting the person settled into their post-injury routine.
There are also injury-specific rehabilitation programs, which target the area affected the most by the injury.